|
|
Risk Management Approach and Risk Profile |
 |
|
|
|
APPROACH TO RISK MANAGEMENT
Strong risk management capabilities are critical to the financial soundness of DBS. The key components of DBS’ risk management approach are: strong risk governance; robust and comprehensive processes to identify, measure, control, monitor and report risks; sound assessments of capital adequacy relative to risks; and a rigorous system of internal control reviews, involving internal and external auditors, as well as reviews and inspections by prudential supervision authorities.
RISK GOVERNANCE
The Group has implemented a framework to give greater clarity, focus and consistency across different risk areas in the governance of risks. Under the DBS Integrated Risk Framework, the Board of Directors, through the Board Risk Management Committee, oversees the establishment of a robust enterprise-wide risk management system and will progressively set risk appetite limits to guide risk-taking within the Group. Management is accountable to the Board for ensuring effective risk management activities and adherence to the risk appetite limits. In this regard, various senior management risk committees provide oversight and forums for discussions on specific risk areas, including Credit Risk, Market Risk, Liquidity Risk and Operational Risk. The committees are the Business Support and Controls Committee, the Group Market Risk Committee, the Group Credit Risk Committee, the Group Asset and Liability Committee, the Group Operational Risk Committee and the Group Commitments and Conflicts Committee.
Business units have primary responsibility for managing specific robust risk exposures. Group Risk Management is the central resource for quantifying and managing the portfolio of risks taken by the Group as a whole. Group Risk Management performs the following roles:
| • |
Develops and implements effective risk and economic capital adequacy assessment frameworks, policies and methodologies |
| • |
Develops and implements an infrastructure that will support DBS’ risk management activities |
| • |
Recommends risk appetite and control limits, in line with the risk governance framework |
| • |
Provides senior management and Board with independent and timely assessment of the aggregate risk profile concerning significant cant risk concentrations, portfolio composition and quality |
| • |
Identifies opportunities to optimise risk-based return on capital |
DBS Group has implemented policies and procedures to identify, measure, analyse and control risk across the firm. A governance framework has been established to provide a disciplined, consistent and tiered approach in the approval of the various risk frameworks/ policies/ procedures throughout the DBS organisation. The framework comprises four levels: Level 1 policies are Board-level approved firm-wide risk frameworks; Level 2 policies are minimum corporate-level and subject-specific risk principles and standards; Level 3 policies are business or location specific in nature; and Level 4 procedures underlie and support the policy implementation. These policies and procedures rely on constant communication, judgment, knowledge of products and markets, and controls by business and support units.
CREDIT RISK
Credit risk is the potential earnings volatility caused by obligors’ inability and/or unwillingness to fulfill their contractual debt obligations. Exposure to credit risks arises primarily from lending activities and also from sales and trading activities, derivatives activities and from participation in payment transactions and securities settlements. Credit exposure includes current as well as potential credit exposure. Current credit exposure is represented by the notional value or principal amount of on-balance sheet financial instruments and off-balance sheet direct credit substitutes, and by the positive market value of derivative instruments. DBS Group also estimates the potential credit exposure over the remaining term of transactions. At DBS Group, a disciplined credit risk management process integrates risk management into the business management processes, while preserving the independence and integrity of risk assessment.
An enterprise-wide Core Credit Risk Policy sets forth the principles by which the Bank and its subsidiaries conduct their credit risk management activities. It ensures credit risk underwriting consistency across the Group, and provides guidance to various credit management units in the formulation of supplementary credit policies specific to their businesses.
The Group Credit Risk Committee serves as an executive forum for discussion and decisions on all aspects of credit risk and its management including the assessment of credit risk taking and adherence to limits, policies, exceptions and other processes; the assessment of the risk-return tradeoffs across the Group; the identification, measurement and monitoring of DBS’ credit risk portfolio, including special loan and asset review situations, specific credit concentrations and credit trends affecting the portfolio; as well as recommendation of credit limits and credit policy at the sector, business and country levels. It will also oversee the ongoing monitoring of various aspects of credit risks within the Basel II framework.
Individual corporate credit risks are analysed and approved by experienced credit officers who consider a number of factors in the identification and assessment of credit risk. Each borrower is assigned a rating under the Counterparty Risk Rating process. For large corporate borrowers, the rating is based on the assessment of all relevant factors including the borrower’s financial condition and outlook, industry and economic conditions, market position, access to capital, and management strength. The Counterparty Risk Rating assigned to smaller business borrowers is primarily based on the borrower’s financial position and strength, which are assessed via the use of a validated quantitative tool.
All ratings are reviewed at least annually and more frequently when conditions warrant. The Counterparty Risk Rating process is further enhanced by the Facility Risk Rating System which takes into consideration facility specific considerations such as credit structuring, collateral, third party guarantees and transfer risks. These credit risk-rating tools are used to assess the credit quality of the portfolio, so that deteriorating exposures are quickly identified and appropriate remedial action can be taken.
Consumer credit risk is managed on a portfolio basis. Business specific credit risk policies and procedures including underwriting criteria, scoring models, approving authorities, regular asset quality review and business strategy review as well as systems, processes and techniques to monitor portfolio performance against benchmarks are in place. Risk models are being used for secured loans to update risk level of each loan on a monthly basis, putting Basel II management principles to daily usage and for regular portfolio quality reviews.
The credit control functions ensure that credit risks are being taken and maintained in compliance with group-wide credit policies and guidelines. These functions ensure proper activation of approved limits, appropriate endorsement of excesses and policy exceptions, and also monitor compliance with credit standards and/or credit covenants established by management and/or regulators.
An independent Credit Risk Review team conducts regular reviews of credit exposures and judgmental credit risk management processes. It also conducts independent validation of internal credit risk rating processes on an annual basis. These reviews provide senior management with objective and timely assessments of the effectiveness of credit risk management practices and ensure group-wide policies, internal rating models and guidelines are being adopted consistently across different business units including relevant subsidiaries.
Stress testing of credit risk has assumed increasing importance in the discipline of credit risk management. DBS uses credit risk stress testing approaches to assess the vulnerability of the portfolio to “exceptional but plausible” adverse credit risk events.
DBS uses various metrics, including Economic Capital-at-Risk, to measure and manage credit concentration risk to individual borrowers, borrower groups and industry sectors. Information on credit exposures by geographical area, business line and industrial classification, and the breakdown of investment and dealing securities are disclosed in Notes 18, 19, 20, 22, 23 and 49 to the Financial Statements and the Management Discussion and Analysis chapter.
COUNTRY RISK
The principles and approach in the management of cross-border risk are spelt out in a Board-approved Country Risk Management Framework. The Framework includes an internal country (and sovereign) risk rating system where the assessments are made independent of business decisions. Benchmark country limits are set to alert the bank when exposures rise to levels that may imply concentration risk. Day-to-day operational country limits, called working limits, are also imposed to manage the shape and growth of the cross-border exposures as they build up. A rigorous scanning process is established, with the objective of adjusting country exposures according to risks perceived at the global, regional and country level. There are close consultations with the businesses and credit management in right sizing cross-border exposures to take into account not only of risks and opportunities, but also the strategic intent of DBS.
TRADING MARKET RISK
Trading market risk arises from changes in pricing parameters, including market rates such as interest rates, foreign exchange rates, equity prices and credit spreads, as well as their correlations and implied volatilities. DBS Group takes trading market risk in the course of market making, structuring and packaging products for investors and issuers, as well as to benefit from market opportunities.
The Trading Market Risk Framework comprises the following elements:
| • |
Types of market risk to be covered, and the risk metrics and methodologies to be used to capture such risks |
| • |
Policies and processes for managing market risks, as well as the roles and responsibilities of relevant functions for the processes |
| • |
Limits to ensure that risk-takers do not exceed aggregate risk and concentration parameters set by senior management and the Board |
| • |
Independent validation of valuation and risk models and methodologies |
| • |
Independent mark-to-market valuation, reconciliation of positions and tracking of stop-loss for trading positions on a timely basis |
| • |
New product/service process whereby risk issues are identified before new products and services are launched |
DBS adopts a Value-at-Risk (VaR) methodology (at a 99% confidence level and a one day holding period) to measure the Group’s trading market risk. In September 2006, the trading book VaR methodology was changed to the historical simulation approach, which is in line with market practice. It takes into account pertinent risk factors and covers all financial instruments which expose the Group to market risk across all geographies. On a daily basis, DBS computes VaR for each trading business unit and location, and at the Group level. The VaR forecasts are backtested against the profit and loss of the trading book in line with the risk model validation policy.
VALUE-AT-RISK AND TRADING INCOME
The following table shows the period-end, average, high and low VaR for the trading risk exposure of the DBSH Group for the period from 1 January 2006 to 31 December 2006.
In $ millions |
As at
31 December 2006 |
Average |
1 January 2006 to
31 December 2006
High |
Low |
 |
Total |
10 |
16 |
28 |
8 |
 |
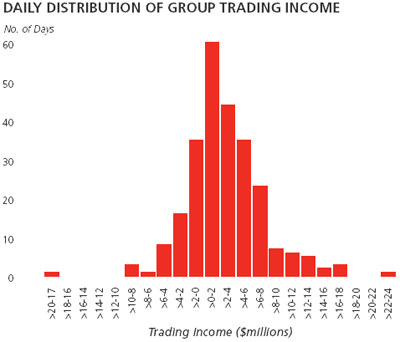
The charts below provide the range of VaR and the daily distribution of trading income in the trading portfolio for the year ended 31 December 2006.
GROUP VaR FOR TRADING BOOK
DBS changed its trading book VaR methodology from Parametric VaR (PVaR) to Historical Simulation VaR (HSVaR) in September 2006. The histogram below is based on PVaR for the period from January to August 2006 and HSVaR from September to December 2006.
|
GROUP VaR FOR TRADING BOOK |
 |
Although VaR provides valuable insights, no single measure can capture all aspects of trading market risk. To complement the VaR framework, regular stress testing is carried out using historical and hypothetical scenarios to monitor the Group’s vulnerability to simultaneous shocks on all market rates. Stress limits are also established accordingly.
The Group Market Risk Committee oversees DBS’ market risk management infrastructure, including framework, policies, processes, information, methodologies and systems. The Committee also sets market risk control limits and provides comprehensive and enterprise-wide oversight of all market risks and their management. In this regard, the Committee meets regularly to review and give direction on the level of market risk taken within DBS Group; its breakdown by desk, geography risk type; trading profit and loss; stress testing results; and risk model backtesting performance.
Information on the Group’s financial assets and liabilities in relation to exposures to interest rate and foreign exchange risks can be found in Notes 46.2(b) and 46.2(c) to the Financial Statements.
STRUCTURAL MARKET RISK
The Group Asset and Liability Committee (“Group ALCO”) oversees the structural interest rate risk, structural foreign exchange risk and funding liquidity risk in the Group. It allocates core limits to regional/local ALCOs in the different countries and ensures that the consolidated exposures of the Group are within prudent levels. Regional/local ALCOs are responsible for managing the risks in their areas including the setting of operational limits and guidelines to fine tune risk management, consistent with the Group’s Asset and Liability Management Policy.
Structural interest rate risk arises from mismatches in the interest rate profile of customer loans and deposits. This interest rate risk has several aspects: basis risk arising from different interest rate benchmarks, interest rate re-pricing risk, yield curve risks and embedded optionality.
To monitor the structural interest rate risk, the tools used by DBS include re-pricing gap reports, sensitivity analysis and income simulations under various scenarios.
In structural foreign exchange exposures, the Group manages the effect of exchange rate movements on its earnings, capital accounts and foreign currency investments. Foreign currency loans/lending and investments in fundable currencies are generally funded with the same foreign currencies. For currencies with high hedging costs or have an illiquid/controlled market, the position will be reviewed by the Structural Foreign Exchange Committee and alternative strategies may be used or left unhedged. Non fundable or illiquid currencies may be hedged with instruments such as non-deliverable forwards.
An Investment Framework governs the Group’s investment of funds. These investments are separately subject to Board and senior management limits on the portfolio size, credit quality, product and sector concentrations and market risk sensitivities under the Framework. Investment market risk is monitored by risk type using sensitivities and by valuation action triggers. Valuation as well as validation of models used in valuation and risk management is carried out by independent support units.
LIQUIDITY RISK
Liquidity risk is the potential earnings volatility arising from being unable to fund portfolio assets at reasonable rates over required maturities. Liquidity obligations arise from withdrawals of deposits, repayments of purchased funds at maturity, extensions of credit and working capital needs. DBS seeks to manage its liquidity to meet its obligations under normal as well as adverse circumstances, and to take advantage of rising lending and investment opportunities.
The primary tool for monitoring liquidity is the maturity mismatch analysis, which is monitored over successive time bands and across major functional currencies. This analysis includes behavioural assumptions on, inter-alia, customer loans, customer deposits and reserve assets. This is tested under normal and adverse market scenario conditions. Limits are established by the Board and senior management for the maximum cumulative cash outflows over successive time bands. Various liquidity ratios, deposit concentration ratios and stress limits are additional tools employed by DBS to manage funding liquidity risk.
As part of its liquidity risk management, DBS Group focuses on a number of components, including tapping available sources of liquidity, preserving necessary funding capacity and contingency planning.
Information on the Group’s financial assets and liabilities in relation to exposures to interest rate risk, foreign exchange risk and liquidity risk can be found in Notes 46.2(b), 46.2(c) and 48 to the Financial Statements.
OPERATIONAL RISK
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people or systems, or from external events. An Operational Risk Management Framework has been developed to ensure that operational risks within the DBS Group are properly identified, monitored, managed and reported in a structured, systematic and consistent manner. A key component of the Framework is a set of Core Operational Risk Standards which provides guidance on the baseline controls to ensure a controlled and sound operating environment. To manage and control operational risk, the Framework is supplemented with various tools including, control self-assessment (CSA), risk event management, key risk indicator monitoring and process risk mapping. Major operational risk mitigation programmes include Business Continuity Management and the Global Insurance Programme.
A firm-wide Operational Risk Management system was implemented in 2006. It is an integrated web-based system, incorporating the individual components of the Framework and facilitates an enhanced analysis and reporting of operational risk data. In addition, a process risk mapping framework was developed to identify the key risks and controls in an end-to-end transaction cycle. Process risk mapping for the major business lines has commenced.
The Group Operational Risk Committee oversees DBS’ operational risk management infrastructure, including the Framework, policies, processes, information, methodologies and systems. The Committee also performs regular review of the operational risk profiles of the Group, and endorses and recommends corporate operational risk policies to be approved by the Business Support & Controls Committee.
The Group Operational Risk function is responsible for implementing the Framework in partnership with the business and support units. The day-to-day operational risk management lies with the business and support units. To reinforce accountability and ownership of risk and control, Unit Operational Risk Managers are appointed to assist the unit heads in driving the overall risk and control agenda and programmes.
As part of Group Audit’s review process, the quality of the operational risk management programmes of the business/ support units are taken into account in assigning a “Management Control Awareness” rating.
BASEL II PREPARATION
DBS views Basel II as a firm-wide programme that will ensure that our credit, market and operational risk management practices continue to meet international best practices. It is an initiative for us to further embed sound risk management practices and culture within our businesses, and ensure that DBS continues to expand our businesses across segments and markets with the right risk management discipline, practices and processes in place. To underscore the importance of this initiative and ensure a concerted effort towards the successful implementation of various aspects of the programme, an integrated Basel II Governance and Programme Management structure is put in place.
A Group Basel II Steering Committee (“Steering Committee”), chaired by the Group CFO, has been set up to oversee the implementation of all programme work streams to ensure that DBS is on track for Basel II qualification. The Steering Committee is supported by sub-committees for each major work stream. Reporting to the Steering Committee, the Basel II Programme Management Office works with the respective work stream sponsors and dedicated project managers to drive the overall Basel II programme.
|
|